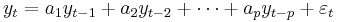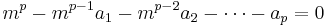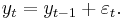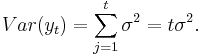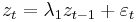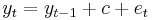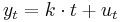Unit root
In time series models in econometrics (the application of statistical methods to economics), a unit root is a feature of processes that evolve through time that can cause problems in statistical inference if it is not adequately dealt with.
A linear stochastic process has a unit root if 1 is a root of the process's characteristic equation. Such a process is non-stationary. If the other roots of the characteristic equation lie inside the unit circle — that is, have a modulus (absolute value) less than one — then the first difference of the process will be stationary.
Contents |
Definition
Consider a discrete time stochastic process { }, and suppose that it can be written as an autoregressive process of order p:
}, and suppose that it can be written as an autoregressive process of order p:
Here, {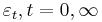 } is a serially uncorrelated, mean zero stochastic process with constant variance
} is a serially uncorrelated, mean zero stochastic process with constant variance 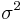 . For convenience, assume
. For convenience, assume 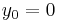 . If
. If 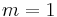 is a root of the characteristic equation:
is a root of the characteristic equation:
then the stochastic process has a unit root or, alternatively, is integrated of order one, denoted 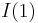 . If m = 1 is a root of multiplicity r, then the stochastic process is integrated of order r, denoted I(r).
. If m = 1 is a root of multiplicity r, then the stochastic process is integrated of order r, denoted I(r).
Example
The first order autoregressive model, 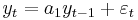 , has a unit root when
, has a unit root when 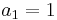 . In this example, the characteristic equation is
. In this example, the characteristic equation is 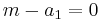 . The root of the equation is
. The root of the equation is 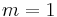 .
.
If the process has a unit root, then it is a non-stationary time series. That is, the moments of the stochastic process depend on 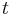 . To illustrate the effect of a unit root, we can consider the first order case, starting from y0=0:
. To illustrate the effect of a unit root, we can consider the first order case, starting from y0=0:
By repeated substitution, we can write 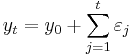 . Then the variance of
. Then the variance of 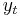 is given by:
is given by:
The variance depends on t since 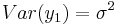 , while
, while 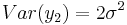 . Note that the variance of the series is diverging to infinity with t.
. Note that the variance of the series is diverging to infinity with t.
Related models
In addition to AR and ARMA models, other important models arise in regression analysis where the model errors may themselves have a time series structure and thus may need to be modelled by an AR or ARMA process that may have a unit root, as discussed above. The finite sample properties of regression models with first order ARMA errors, including unit roots, have been analyzed.[1][2]
Estimation when a unit root may be present
Often, ordinary least squares (OLS) is used to estimate the slope coefficients of the autoregressive model. Use of OLS relies on the stochastic process being stationary. When the stochastic process is non-stationary, the use of OLS can produce invalid estimates. Granger and Newbold[3] called such estimates 'spurious regression' results: high R2 values and high t-ratios yielding results with no economic meaning.
To estimate the slope coefficients, one should first conduct a unit root test, whose null hypothesis is that a unit root is present. If that hypothesis is rejected, one can use OLS. However, if the presence of a unit root is not rejected, then one should apply the difference operator to the series. If another unit root test shows the differenced time series to be stationary, OLS can then be applied to this series to estimate the slope coefficients.
For example, in the AR(1) case, 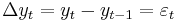 is stationary.
is stationary.
In the AR(2) case, 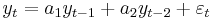 can be written as
can be written as  where L is a lag operator that decreases the time index of a variable by one period:
where L is a lag operator that decreases the time index of a variable by one period: 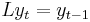 . If
. If 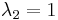 , the model has a unit root and we can define
, the model has a unit root and we can define 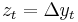 ; then
; then
is stationary if 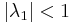 . OLS can be used to estimate the slope coefficient,
. OLS can be used to estimate the slope coefficient, 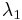 .
.
If the process has multiple unit roots, the difference operator can be applied multiple times.
Properties and characteristics of unit-root processes
- Shocks to a unit root process have permanent effects which do not decay as they would if the process were stationary
- As noted above, a unit root process has a variance that depends on t, and diverges to infinity
- If it is known that a series has a unit root, the series can be differenced to render it stationary. For example, if a series
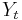 is I(1), the series
is I(1), the series 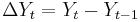 is I(0) (stationary). It is hence called a difference stationary series.
is I(0) (stationary). It is hence called a difference stationary series.
Unit root hypothesis
Economists[4][5][6][7] debate whether various economic statistics, especially output, have a unit root or are trend stationary. A unit root process with drift is given in the first-order case by
where c is a constant term referred to as the "drift" term, and 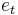 is white noise. Any non-zero value of the noise term, occurring for only one period, will permanently affect the value of
is white noise. Any non-zero value of the noise term, occurring for only one period, will permanently affect the value of 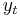 as shown in the graph, so deviations from the line
as shown in the graph, so deviations from the line 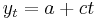 are non-stationary; there is no reversion to any trend line. In contrast, a trend stationary process is given by
are non-stationary; there is no reversion to any trend line. In contrast, a trend stationary process is given by
where k is the slope of the trend and 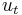 is noise (white noise in the simplest case; more generally, noise following its own stationary autoregressive process). Here any transient noise will not alter the long-run tendency for
is noise (white noise in the simplest case; more generally, noise following its own stationary autoregressive process). Here any transient noise will not alter the long-run tendency for 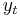 to be on the trend line, as also shown in the graph. This process is said to be trend stationary because deviations from the trend line are stationary.
to be on the trend line, as also shown in the graph. This process is said to be trend stationary because deviations from the trend line are stationary.
The issue is particularly popular in the literature on business cycles.[8][9] Research on the subject began with Nelson and Plosser[10] whose paper on GNP and other output aggregates failed to reject the unit root hypothesis for these series. Since then, a debate—entwined with technical disputes on statistical methods—has ensued. Some economists[11] argue that GDP has a unit root or structural break, implying that economic downturns result in permanently lower GDP levels in the long run. Other economists argue that GDP is trend-stationary: That is, when GDP dips below trend during a downturn it later returns to the level implied by the trend so that there is no permanent decrease in output. While the literature on the unit root hypothesis may consist of arcane debate on statistical methods, the implications of the hypothesis can have concrete implications for economic forecasts and policies.
See also
- Dickey–Fuller test
- Augmented Dickey–Fuller test
- Unit root test
- Phillips–Perron test
- Cointegration, determining the relationship between two variables having unit roots
- Weighted symmetric unit root test (WS)
- Kwiatkowski, Phillips, Schmidt, Shin test, known as KPSS tests
Notes
- ^ Sargan, J.D. and Alok Bhargava (1983). "Testing residuals from least squares regressions for being generated by the Gaussian random walk", Econometrica, 51,153-174.
- ^ Sargan J.D. and Alok Bhargava (1983). "Maximum likelihood estimation of regression models with first order moving average errors when the root lies on the unit circle", Econometrica, 51, 799-820
- ^ Granger, C. W. J. and Newbold, P. (1974). "Spurious regressions in econometrics". Journal of Econometrics 2: 111–120. doi:10.1016/0304-4076(74)90034-7.
- ^ http://www.econbrowser.com/archives/2009/03/trend_stationar.html
- ^ Krugman, Paul. "The conscience of a liberal". http://krugman.blogs.nytimes.com/2009/03/03/roots-of-evil-wonkish/
- ^ http://econlog.econlib.org/archives/2009/03/greg_mankiw_get.html "Greg Mankiw gets technical"
- ^ Steve Verdon, "Economic Cage Match: Mankiw vs. Krugman" http://www.outsidethebeltway.com/economic_cage_match_mankiw_vs_krugman/
- ^ Hegwood, Natalie, and Papell,David H. "Are real GDP levels trend, difference, or regime-wise trend stationary? Evidence from panel data tests incorporating structural change." http://www.uh.edu/~dpapell/realgdp.pdf
- ^ Lucke, Bernd. "Is Germany‘s GDP trend-stationary? A measurement-with-theory approach." http://www.wiso.uni-hamburg.de/fileadmin/wiso_vwl_iwk/paper/gdptrend.pdf
- ^ Nelson, Charles R. and Plosser, Charles I. (1982), "Trends and Random Walks in Macroeconomic Time Series: Some Evidence and Implications," Journal of Monetary Economics, 10, 139-162.
- ^ Olivier Blanchard with the International Monetary Fund makes the claim that after a banking crisis "on average, output does not go back to its old trend path, but remains permanently below it."